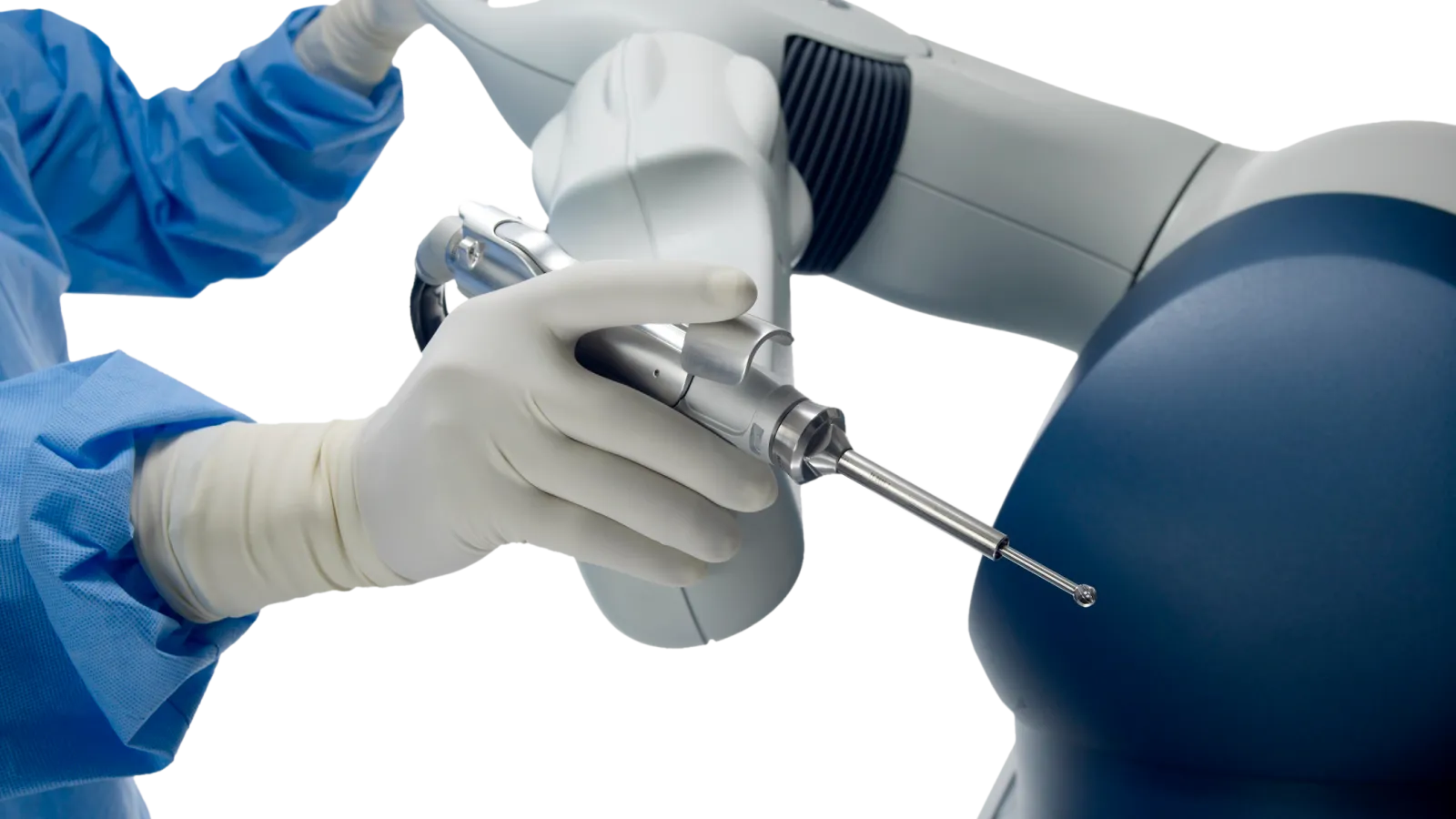
Robot-Assisted Knee Replacement
in Lexington, KY
Knee Replacement Doctors in Kentucky
Experience Precision Knee Replacement Surgery with Mako SmartRobotics™
At Bluegrass Orthopaedics, our knee specialists Dr. Ched Crouse, Dr. Kevin Denehy, Dr. Greg D'Angelo, Dr. Wallace Huff, Dr. Owen McGonigle, and Dr. Eric Schafer are performing knee replacements using the Mako robotic-arm assisted technology at the Bluegrass Specialty Surgery Center. Robotic-assisted surgery requires advanced training and certification and provides additional precision, less soft-tissue trauma, less postoperative pain, potentially quicker recovery, better knee function, and improved patient satisfaction.
What are the Benefits of Robotic Knee Replacement Surgery?
Your dedicated Bluegrass Orthopaedics team can walk you through every aspect of the surgery before your procedure. Some benefits of robotic knee replacement surgery include:
- Minimal trauma to the surrounding tissues
- Faster recovery time
- Less postoperative pain
- Minimal scarring
- Outpatient surgery
- Reduced blood loss and need for transfusion
- Improved Long-term outcomes

Mako Robotic-Assisted Videos
BGO & BSSC Welcomes the Mako™ Robot

Mako Robot Patient Testimony

Mako Robot Webinar

Mako Robotic-Assisted
Total Joint Animation
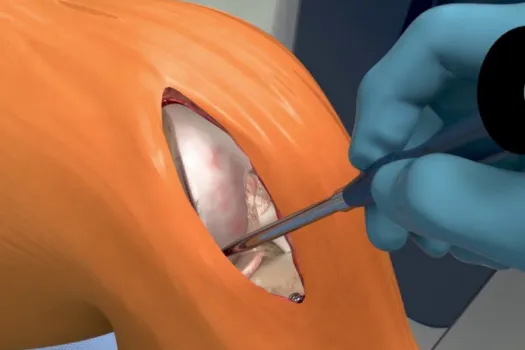
Mako Robotic-Assisted
Total Joint Patient Testimonial

Outpatient Knee Surgery with
Mako Smart Robotics™
- Through CT-based 3D modeling of bone anatomy, Bluegrass Orthopaedic surgeons use the Mako System to create a personalized surgical plan.
- The Mako SmartRobotics™ for knee replacement is the only robotic-arm-assisted surgical technology featuring AccuStop™ haptic technology. It offers visual, auditory, and tactile feedback to help limit soft tissue damage during surgery.
- Mako SmartRobotics™ is associated with reduced pain, fewer opiate analgesics, less inpatient physical therapy, shorter hospital stays, improved knee flexibility, and better soft tissue protection than manual techniques.

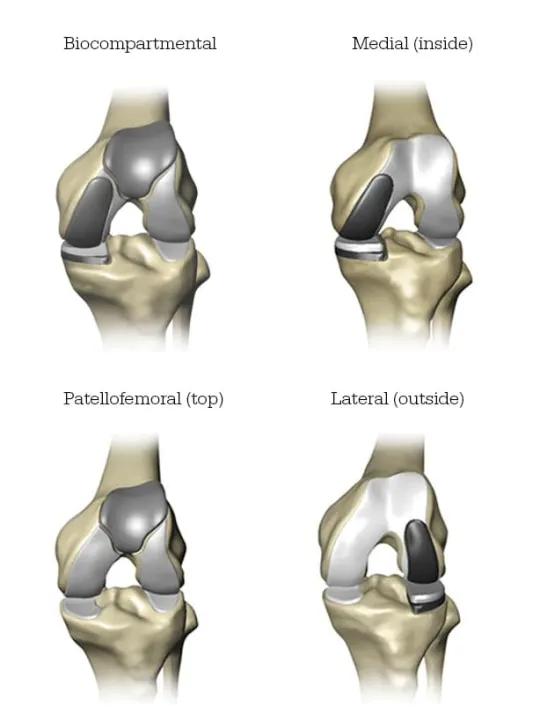
What’s the Difference Between a Total Knee and Partial Knee Replacement?
If a patient has severe arthritis in their knee, a surgeon may recommend total or partial knee replacement. Mako SmartRobotics™ for Partial Knee replacement is a treatment option for adults in the early-to-mid stage of osteoarthritis (OA) that has not yet affected all three knee compartments. Depending on where the arthritis is affecting the knee, patients may have an implant inserted in any of the following areas:
In a unicondylar knee replacement, only one area or compartment of the knee joint is replaced. A patellofemoral knee replacement involves replacing both the kneecap (or patella) and the groove at the lower end of the thigh bone (or femur). On the other hand, a bicompartmental knee replacement involves replacing two compartments of the knee—the inside (medial) and the kneecap.
Mako SmartRobotics™ for Total Knee replacement is a medical procedure that can treat adults with mid to late-stage osteoarthritis in their knee. The surgeon replaces the entire knee joint during the procedure and inserts a Triathlon Total Knee implant. Unlike traditional knee replacements, Triathlon knee replacements are designed to work with the body to promote a natural-like circular motion. This implant has over a decade of clinical history and is considered a reliable treatment option.
Mako SmartRobotics™ Orthopedic Expertise at Bluegrass Orthopaedics
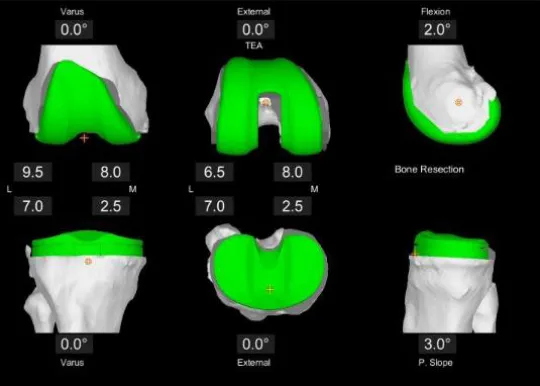
Personalized Surgical Plan: Before knee surgery, a CT scan is taken to create a 3D virtual model of your knee joint. Your orthopedic surgeon then uses this model to assess your bone structure, disease severity, joint alignment, and surrounding bone and tissue. Based on this evaluation, your surgeon will determine your implant's appropriate size, placement, and alignment to ensure the best possible outcome for your knee surgery.
Range-of-Motion Assessment: During your procedure, Mako provides your orthopedic surgeon with real-time data, enabling them to continuously assess the movement and tension of your new joint and make any necessary adjustments to your surgical plan.
Arthritic Bone Removal: During the surgery, your orthopedic surgeon will use Mako's robotic arm to remove the arthritic bone and cartilage from your knee precisely. This process is guided by a virtual boundary that provides tactile resistance to help the surgeon stay within the limits defined in your surgical plan. Once the diseased bone is removed, the implant will be placed into the knee joint. After the successful implant placement, you will be taken to the recovery room, where your journey to strengthen your new joint will begin.
Outpatient Knee Surgery with Mako SmartRobotics™ in Lexington, KY
At Bluegrass Orthopaedics in Lexington, KY, we specialize in precision knee replacement surgery using state-of-the-art Mako SmartRobotics™ technology. Our team is committed to delivering exceptional care and superior outcomes to our patients, led by experienced knee specialists Dr. Ched Crouse, Dr. Kevin Denehy, Dr. Greg D'Angelo, Dr. Wallace Huff, Dr. Owen McGonigle, and Dr. Eric Schafer.
Mako SmartRobotics™ Certified Physicians
References
- Anthony I, Bell SW, Blyth M, Jones B et al. Improved accuracy of component positioning with robotic-assisted unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016;98-A(8):627-35.
- Illgen, R, Bukowski, B, Abiola, R, Anderson, P, Chughtai, M, Khlopas, A, Mont, M. Robotic-assisted total hip arthroplasty: Outcomes at minimum two year follow up. Surgical Technology International. 2017 July 25; 30:365-372.
- Mahoney O, Kinsey T, Mont M, Hozack W, Orozco F, Chen A. Can computer generated 3D bone models improve the accuracy of total knee component placement compared to manual instrumentation: a prospective multi-center evaluation? International Society for Technology in Arthroplasty 32nd Annual Congress. Toronto, Canada. October 2-5, 2019.
- Suarez-Ahedo, C; Gui, C; Martin, T; Chandrasekaran, S; Domb, B. Robotic arm assisted total hip arthoplasty results in smaller acetabular cup size in relation to the femoral head size: A Matched-Pair Controlled Study. Hip Int. 2017; 27 (2): 147-152.
- Haddad, F.S, et al. Iatrogenic Bone and Soft Tissue Trauma in Robotic-Arm Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty Compared With Conventional Jig-Based Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Prospective Cohort Study and Validation of a New Classification System. J Arthroplasty. 2018 Aug;33(8):2496-2501. Epub 2018 Mar 27.
- Hozack WJ, Chen AF, Khlopas A, et al. Multicenter analysis of outcomes after robotic-arm assisted total knee arthroplasty. Presented at: The Knee Society (TKS) 2018 Members Meeting; September 20-22, 2018; Saint Louis, MO.
- Banks, Scott A, PhD. Haptic Robotics Enable a Systems Approach to Design of a Minimally Invasive Modular Knee Arthroplasty. Am J Orthop. 2009;38(2 suppl):23-27. February 2009.
- Hampp E, Chang TC, Pearle A. Robotic partial knee arthroplasty demonstrated greater bone preservation compared to robotic total knee arthroplasty. Annual Orthopaedic Research Society. Austin, TX. 2-5 Feb 2019.




